Anatomy Of Pineal Gland
Pineal Gland Anatomy The pineal gland is a pine-cone shape located midline the brain structure that is unpaired and lies between the laterally positioned thalamic bodies and behind the habenular commissure. The pineal gland is placed in the quadrigeminal cistern adjacent to the corpora quadrigemina.
 The Bulletin Feeding The Pineal Gland Pineal Gland Gland Pituitary Gland
The Bulletin Feeding The Pineal Gland Pineal Gland Gland Pituitary Gland
This gland develops from brain section diencephalon and located behind the third cerebral ventricle bathed in cerebrospinal fluid.

Anatomy of pineal gland. The pineal gland is a small reddish-gray structure composed of gray matter. Melatonin influences sexual development and sleep-wake cycles. There is no consensus regarding the volume of the pineal gland in humans.
The pineal gland or pineal body is a small pine-cone shaped organ that lies within the roof of the third ventricle deep within the brain. It is attached by a stalk to the posterior wall of third ventricle. Normal sizes have been described in the radiology literature up to 14 mm 9.
Since the discovery of melatonin approximately 25 years ago there has been intense study regarding the details of the structure and function of the pineal gland. The pineal gland is composed of pinealocytes and supporting cells that resemble the astrocytes present in the brain. The adrenergic nerves entering the pineal gland regulate its functions.
A structure of the diencephalon of the brain the pineal gland produces the hormone melatonin. The principal aspect of the pineal gland anatomy is the pineal parenchymal cell or pinocyte. Overview In human the cycles of sleep and wakefulness usually mimics the rhythm of light and dark.
Above is the habenular commissure and below it is the posterior commissure. Embryology derivated from two merged parts. Anatomy physiology and clinical significance.
Anatomy of the Pineal Gland The pineal gland is a composed of specialized epithelial-like cells known as pineocytes pinocytes. The pineal gland is present in the epithalamus between the two hemispheres tucked in the groove of the thalamus join. Pineal glandANTOMY HISTOLOGYFUNCTION 1.
In close proximity to the gland are the superior colliculi of the midbrain paired structures that play an important role in vision. Erlich SS Apuzzo ML. The pineal gland develops during the second month of gestation as a diverticulum in the diencephalic.
The pineal gland typically measures around 7 x 6 x 3 mm in size and is situated in a groove between the laterally placed thalamic bodies 1-6. The pineal gland is a neuroendocrine organ that comprises a part of the epithalamus one of the three divisions of the diencephalon. Take our quiz on the thalamus and its surrounding stru.
The pineal gland produces melatonin a serotonin -derived hormone which modulates sleep patterns in both circadian and seasonal cycles. The pineal gland is essentially an extra-axial structure and it is surrounded by the posterior commissure ventrally the corpus callosum superiorly and the habenular commissure dorsally. The pinealocyte cells that make up the pineal gland are known to produce and secrete the amine hormone melatonin which is derived from serotonin.
Other components of the epithalamus are the stria medullaris habenular nuclei posterior commissure and paraventricular nuclei. The pineal gland is an endocrine gland located in the epithalamus near the center of the human brain. Anatomy of Pineal Gland The pineal gland is about 03 inches long and weighs 01 grams.
The pineal gland found inferior but somewhat posterior to the thalamus is a tiny endocrine gland whose functions are not entirely understood. Autopsy studies have shown that the average size of the pineal gland is similar to a grain of rice. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone and gives it its name.
These cells have long processes with makes contact with certain types or nerve cells known as astrocytes. At fourth week of life as a median evagination of the caudal end of the diencephalon roof. MRI of the brain magnification T1-weighted axial view.
One contributing factor to this phenomenon is the activity of a small cone- like flattened body called the pineal gland or the epiphysis cerebri. Anatomy of the pineal gland The pineal gland develops from the roof of the diencephalon a section of the brain and is located behind the third cerebral ventricle in the brain midline between the two cerebral hemispheres. The pineal gland is composed of cells called pinealocytes and cells of the nervous system called glial cells.
The pineal gland connects the endocrine system with the nervous system in that it converts nerve signals from the sympathetic system of the peripheral. As it is one of the endocrine glands it secretes its product the hormone called melatonin directly into the blood. The pineocytes have photosensory capabilities meaning that it is sensitive to light.
Its name is derived from its shape which is similar to that of a pinecone Latin pinea. Sleep patterns are considered to be modulated by this hormone as its production is stimulated by the absence of light. Upper part of pineal gland is in continuity with the habenula containing the little habenular nucleus- also called anterior peduncle lower part is in continuity with the posterior commissure.
The pineal gland conarium or epiphysis cerebri is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. This work is reviewed with particular emphasis on those aspects of importance to human. The pineal gland is a midline structure located between the two cerebral hemispheres.
Appearing to arise from the gland are two laminae. Pineal gland This photo gallery presents the anatomy of pineal gland by means of MRI T1-weighted sagittal axial and coronal views. Definition location and function of this endocrine gland.
This video covers the pineal gland anatomy. The pineal gland is a small pinecone-shaped gland of the endocrine system.
 Pineal Gland Secretes Hormore Melatonin Pineal Gland Gland Endocrine System
Pineal Gland Secretes Hormore Melatonin Pineal Gland Gland Endocrine System
 The Pineal Gland Is Undergoes Involution Meaning That It Atrophies Or Decreases In Size Over Time The Thymus Does This As Pineal Gland Endocrine System Gland
The Pineal Gland Is Undergoes Involution Meaning That It Atrophies Or Decreases In Size Over Time The Thymus Does This As Pineal Gland Endocrine System Gland
 Pineal Gland Anatomical Cross Section Vector Illustration Diagram With Human Brains Medical Information Poster Cross Pineal Gland Decalcify Pineal Gland Gland
Pineal Gland Anatomical Cross Section Vector Illustration Diagram With Human Brains Medical Information Poster Cross Pineal Gland Decalcify Pineal Gland Gland
 Hormones Released From Pituitary Gland And Their Functions Pituitary Gland Endocrine System Gland
Hormones Released From Pituitary Gland And Their Functions Pituitary Gland Endocrine System Gland
 Neuroanatomy Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Brain Anatomy
Neuroanatomy Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Brain Anatomy
 The Pineal Gland Is Part Of A Complex And Fascinating System Pineal Gland Human Anatomy Art Gland
The Pineal Gland Is Part Of A Complex And Fascinating System Pineal Gland Human Anatomy Art Gland
 Pineal Gland Location In Real Brain Google Search In 2020 Brain Anatomy Pineal Gland Gland
Pineal Gland Location In Real Brain Google Search In 2020 Brain Anatomy Pineal Gland Gland
 Pineal Gland Human Anatomy Reference Library Redorbit Pineal Gland Facts Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland
Pineal Gland Human Anatomy Reference Library Redorbit Pineal Gland Facts Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland
 Find Out What Is The Pineal Gland And What Does It Do What Is Calcified Pineal Gland And Pineal Gland Cyst Role Of Brain Diagram Pineal Gland Brain Learning
Find Out What Is The Pineal Gland And What Does It Do What Is Calcified Pineal Gland And Pineal Gland Cyst Role Of Brain Diagram Pineal Gland Brain Learning
 The Entire Function Of The Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Hormone Replacement Therapy Growth Hormone
The Entire Function Of The Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Hormone Replacement Therapy Growth Hormone
 Pin Na Doske Supplements For Us
Pin Na Doske Supplements For Us
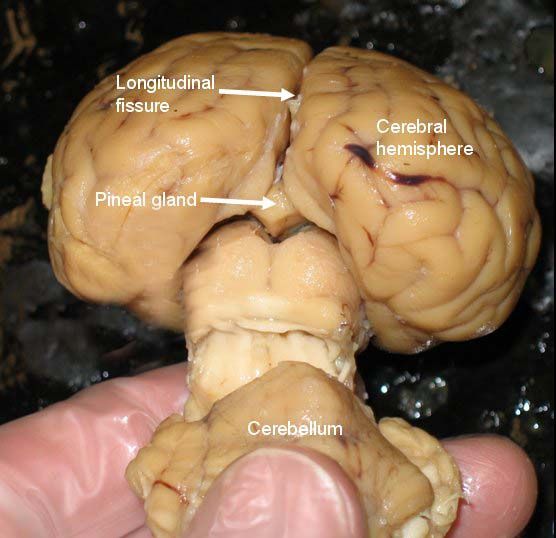 Anatomy Pineal Gland Pineal Gland Gland Body Healing
Anatomy Pineal Gland Pineal Gland Gland Body Healing
 Humans Are Bestowed With A Certain Part Of Their Brain Known As The Pineal Gland Or Also Known As Our Third Eye Brain Diagram Human Brain Anatomy Brain Anatomy
Humans Are Bestowed With A Certain Part Of Their Brain Known As The Pineal Gland Or Also Known As Our Third Eye Brain Diagram Human Brain Anatomy Brain Anatomy
 Position Of The Pineal Gland Somatic Sensation Caudate Nucleus Pearson Education
Position Of The Pineal Gland Somatic Sensation Caudate Nucleus Pearson Education
 Also He Jung Spoke Of His Great Interest On Reading That A Neuro Surgeon Concerned With Epilepsy Had Stim Pineal Gland Nervous System Anatomy Brain Anatomy
Also He Jung Spoke Of His Great Interest On Reading That A Neuro Surgeon Concerned With Epilepsy Had Stim Pineal Gland Nervous System Anatomy Brain Anatomy
 Pineal Gland Human Anatomy Organs Pineal Gland Anatomy Organs Human Anatomy And Physiology
Pineal Gland Human Anatomy Organs Pineal Gland Anatomy Organs Human Anatomy And Physiology
 Cross Section Of Brain Showing The Pituitary And Pineal Glands Cerebellum And Sponsored Sponsored Ad Section Pineal Gland Gland Graphic Art Prints
Cross Section Of Brain Showing The Pituitary And Pineal Glands Cerebellum And Sponsored Sponsored Ad Section Pineal Gland Gland Graphic Art Prints
 Pin By Rachael Wood On Love Pineal Gland Gland Craniosacral Therapy
Pin By Rachael Wood On Love Pineal Gland Gland Craniosacral Therapy

Post a Comment for "Anatomy Of Pineal Gland"