Ankle X Ray Anatomy
217 computed tomography CT or magnetic resonance imaging MRI may be required to identify minimally displaced ankle fractures. Joints of Foot and Ankle.
 Pin By Manumpan Sihombing On Radiology Impingement Ankle Radiology
Pin By Manumpan Sihombing On Radiology Impingement Ankle Radiology
Forcing the foot to dorsiflex can be painful and may cause additional injuries.

Ankle x ray anatomy. Frank Smithuis and Robin Smithuis. Oblique projections 1 plain radiograph tomography Fig. Normal Foot and Ankle X Ray Anatomy.
The following subjects will be discussed. The rearfoot is is composed of the talus and the calcaneus heel bone. AP view right ankle127.
Presentation Outline Relevant anatomy X ray positioning Interpretation of X rays Lines and angles Relevant pathology 3. Intro to ankle x-rays013. The Ankle is comprised of the talus the tibia and the fibula.
A doctor puts pressure on an injured ankle and takes an X-ray. Standard axial coronal and sagittal planes are used in the ankle both on 15T and in 3T. When calcaneal pathology is suspected an additional image can be made in axial direction.
It should be noted though that in some countries including the UK only the mortise and lateral are used. In this article a systematic approach is presented on how to describe a standard MRI of the ankle. Radiologists perform ankle imaging to assess injuries of the foot and ankle anatomy.
Depending on the request various images can be made. AP View Before performing an x-ray examination of the ankle technologist must evaluate the ankle condition to avoid additional injuries. This joint is a main contributor of stability in the lower limbs and it allows humans to perform actions such as running jumping and walking 1 2.
37Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI The ankle is the joint that is located between the leg and the foot. The distal tibia and fibula articulate with each other at the distal tibiofibular joint which is more commonly referred to as the tibiofibular syndesmosis or simply the syndesmosis. Radiologists perform ankle imaging to assess injuries of the foot and ankle anatomy.
The rear foot the mid foot and the forefoot. A standard series includes an anteroposterior AP image a Mortise image and a lateral image. This video tutorial presents the anatomy of ankle x-rays000.
Experts analyze the different imaging techniques to identify better diseases associated with the foot and ankle including diabetic foot ulcers and abnormal growths in the foot and ankle1. Anatomy of the ankle. Standard ankle series for x-rays020.
The foot and ankle can be subdivided into 4 different parts. See the annotated images below from WikiFoundry and thanks also to Radiopaedia. Excellent view of posterior subtalar joint given by these views helps in intraoperative monitoring of calcaneus fracture reduction and assessment of.
The mortise view is the true AP projection of the ankle joint. The tibia and fibula make up just above the ankle. Ankle injuries may involve bones or ligaments in isolation or a combination of bones and ligaments.
In addition to the standard planes a oblique scan is sometimes included oriented perpendicular to the peroneus and tibialis posterior tendons. Radiology department of the Amsterdam University Medical Centre in Amsterdam and Alrijne hospital in Leiderdorp in the Netherlands. This is an online quiz called Anatomy of the Ankle X-Ray There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper.
In this image you will find Tibia Inferior articular surface Ankle joint Medial malleolus Lateral malleolus Trochlea of talus Body Talus Lateral process Neck Tarsal sinus Head Talocalcaneonavicular joint Navicular Cuneonavicular joint Sustentaculum tali Talar Sheff Medial cuneiform Calcaneocuboid. X ray of foot and ankle 1. Use a methodical approach such as ABCs to look at a radiograph.
Interpreting an ankle X-ray. Ideally you should be able to see at least the distal third of the tibia and fibula and the talus on the mortise view and in addition to those you should be able to see the calcaneum and the base of the 5 th metatarsal on the lateral view. X-ray of the Ankle.
The patient can remain supine with an image receptor placed vertically adjacent to the lateral aspect of the upright ankle and the x-ray beam is directed horizontally centered at the bony prominence of the medial malleolus of the distal tibia. The ankle is a synovial joint composed of the distal tibia and fibula as they articulate with the talus. A true AP projection of the ankle is the malleoli is not the same distance from the image receptor in the anatomic position.
The ankle x-ray is used primarily to demonstrateexclude a fracture. MRI examination of the ankle. Same horizontal plane as the medial malleolus and both are parallel to the x-ray tabletop.
X-rays directly visualise bone injury but understanding of the anatomical position of ligaments is required to appreciate the presence of ligament injuries which are not directly visualised. These views are taken with 10 20 30 and 40 degrees cranial angulation of an X-ray beam focused at the tip of the fibula with ankle rotated 45 degrees internally. Foot ankle X-ray lateral view.
X ray of foot and ankle Dr Sulav Pradhan MD Resident Radiodiagnosis NAMS Kathmandu Nepal 2. Experts analyze the different imaging techniques to identify better diseases associated with the foot and ankle including diabetic foot ulcers and abnormal growths in the foot and ankle 1. An X-ray film of the ankle is most commonly used to determine a fracture arthritis or other problems.
An x-ray of the ankle will have three views AP mortise and lateral.
 Please Tag If You Wish To Share Theradiologist Radiology Radiologist Physician Physicianassistant Medici Radiology Radiology Student Medical Anatomy
Please Tag If You Wish To Share Theradiologist Radiology Radiologist Physician Physicianassistant Medici Radiology Radiology Student Medical Anatomy
 Ankle Fracture X Ray Stock Photos Royalty Free Royalty Free Photos Ankle Fracture X Ray Medical School Stuff
Ankle Fracture X Ray Stock Photos Royalty Free Royalty Free Photos Ankle Fracture X Ray Medical School Stuff
 Fratture Di Caviglia Caviglia Rotta Rottura Di Collo Piede Dr G Fanzone Radiography Ankle Fracture Medical Radiography
Fratture Di Caviglia Caviglia Rotta Rottura Di Collo Piede Dr G Fanzone Radiography Ankle Fracture Medical Radiography
 Radiographic Anatomy Of The Skeleton Ankle Mortise View Labelled Radiology Student Radiography Student Radiology Schools
Radiographic Anatomy Of The Skeleton Ankle Mortise View Labelled Radiology Student Radiography Student Radiology Schools
 Arteries And Bones Of The Lower Extremity Interactive Atlas Of Human Anatomy Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Radiology
Arteries And Bones Of The Lower Extremity Interactive Atlas Of Human Anatomy Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Radiology
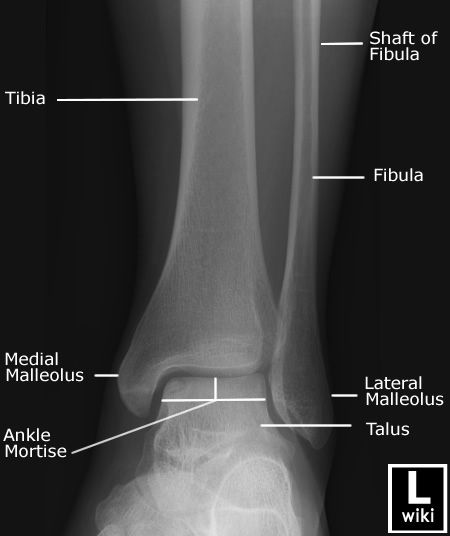 Ankle Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography Radiology Radiology Student Radiology Schools
Ankle Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography Radiology Radiology Student Radiology Schools
 Ankle Joint Radiogram E Anatomy Lower Limb Conventional Radiology X Ray E Anatomy Images Media Imaios Radiography Radiography Student Radiology Tech
Ankle Joint Radiogram E Anatomy Lower Limb Conventional Radiology X Ray E Anatomy Images Media Imaios Radiography Radiography Student Radiology Tech
 Ankle Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Medical Knowledge
Ankle Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Medical Knowledge
 Radiographic Anatomy Of The Skeleton Ankle Lateral View Labelled Medical Knowledge Radiology Student Radiology
Radiographic Anatomy Of The Skeleton Ankle Lateral View Labelled Medical Knowledge Radiology Student Radiology
 Bohlers Angle On Xray For Calcaneus Fractures Radiology Medical Anatomy X Ray
Bohlers Angle On Xray For Calcaneus Fractures Radiology Medical Anatomy X Ray
 Radioanatomy Of The Ankle Radiology Of The Ankle Lateral View With Anatomical Structures Labeled As Calcaneus Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Radiology
Radioanatomy Of The Ankle Radiology Of The Ankle Lateral View With Anatomical Structures Labeled As Calcaneus Radiology Student Medical Anatomy Radiology
 Radiograph X Ray Of The Ankle Anatomy On An Anterior View Showing Tibia Fibula Talus Lateral And Medial Malle Anatomy Medical Anatomy Diagnostic Imaging
Radiograph X Ray Of The Ankle Anatomy On An Anterior View Showing Tibia Fibula Talus Lateral And Medial Malle Anatomy Medical Anatomy Diagnostic Imaging
 Pin By Shayma On Bones Foot Anatomy Medical Anatomy Anatomy
Pin By Shayma On Bones Foot Anatomy Medical Anatomy Anatomy
 Foot Oblique Unidad Especializada En Ortopedia Y Traumatologia Www Unidadortopedia Com Pbx 6923370 Bogo Radiology Student Radiology Schools Medical Knowledge
Foot Oblique Unidad Especializada En Ortopedia Y Traumatologia Www Unidadortopedia Com Pbx 6923370 Bogo Radiology Student Radiology Schools Medical Knowledge
 Lateral View Of The Foot On Radiography X Ray Metatarsals Phalanx Cuboid Navicular Cuneiform Bones Medical Radiography Radiology Student Anatomy
Lateral View Of The Foot On Radiography X Ray Metatarsals Phalanx Cuboid Navicular Cuneiform Bones Medical Radiography Radiology Student Anatomy
 Pin On Run Run And Never Look Back
Pin On Run Run And Never Look Back



Post a Comment for "Ankle X Ray Anatomy"