Anatomy Of The Eye (major Landmarks And Features 1 Of 3)
Externally the epithelial cell border between conjunctiva and cornea possesses multipotential cells importan. A colored circular muscle the iris which is beautifully pigmented giving us our eyes color the central aperture of the iris is the pupil Fig.
 Image Result For Vaporize In Circuit
Image Result For Vaporize In Circuit
The cephalon or cephalic region refers to the head.

Anatomy of the eye (major landmarks and features 1 of 3). The forebrain has two major parts called the diencephalon and the telencephalon. The acromial end houses a small facet for articulation with the acromion of the scapula at the acromioclavicular joint. Through a simple and intuitive interface it is possible to observe every anatomical structure from any angle.
Each of these bones has distinctive features that contribute to the surface landmarks of the facethe orbital rims zygomatic arch the mastoid process and the mentum. If one wears contact lenses the contact lens rests on the cornea. The main purpose of the cornea is to help focus light as it enters the eye.
View of the human eye. There also is a test for color deficiency and three short quizzes. Microscopic anatomy is the study of tiny anatomical structures such as tissues and cells.
This resource includes descriptions functions and problems of the major structures of the human eye. Highly detailed 3D models with textures up to 4k resolution enable to examine the shape of each structure of the human body with great depth. The thoracic spine is the second segment of the vertebral column located between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae.
Anatomy of the Eye Major Landmarks and Features 2 of 3 Reset Help Ora serata ID Cillary body Fom Palpebral conjunctiva Cuan muscle Ocular conjunctive process. This area is further differentiated into the cranium skull facies face frons forehead oculus eye area auris ear bucca cheek nasus nose oris mouth and mentum chin. Conjunctiva cornea iris lens macula retina optic nerve vitreous and extraocular muscles.
The forebrain the midbrain and the hindbrain are the three main parts of the brain. There are two major types of anatomy. The midbrain also called the mesencephalon connects the.
The iris is the colored part of the eye. The surface anatomy of the face is best appreciated by referring to the bony landmarks of the frontal maxillary zygomatic and mandibular bones. Here are the main body landmarks of anatomy.
Anatomy of the Eye Major Landmarks and Features 1 of 3 Optic disc Central retinal artery and vein Retina Fovea Posterior cavity with vitreous body Choroid Sclera Optic nerve. The frontal region of the cranium is the forehead covering the frontal region is the frontalis muscle which overlies the frontal bone the frontal region terminates at the superciliary arches. The sclera is continuous with the cornea.
Upgrade to remove ads. Gross macroscopic anatomy is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye such as the external and internal bodily organs. Study with Flashcards again.
Sclera - The sclera is the white tough outer covering of globe of the eye. The iris acts like a diaphragm that controls the amount of light allowed into the eye. It also serves as an attachment point for two ligaments.
Cranium can be subdivided into three regions each having prominent surface anatomy features. The pupil serves as an aperture which is adjusted by the surrounding iris acting as a diaphragm that regulates the amount of light entering the eye. Anatomy of the Eye Major Landmarks and Features 3 of 3 Cores Pub Coreal dimma Amenor came with or home Apple iPhone Get more help from Chegg Get 11 help now from expert Anatomy and Physiology tutors.
This circular muscle controls the size of the pupil so that more or less light depending on conditions is allowed to enter the eye. The limbus forms the border between the transparent cornea and opaque sclera contains the pathways of aqueous humour outflow and is the site of surgical incisions for cataract and glaucoma. Iris - The iris is a pigmented tissue with two muscles that control pupil constriction and pupil dilation.
It consists of twelve vertebrae which are separated by fibrocartilaginous intervertebral discs. The forebrain is responsible for a number of functions related to thinking perceiving and evaluating sensory information. 13-6 Cranium Cranium cranial region or braincase is covered by the scalp which is composed of skin and subcutaneous tissue.
The anatomy of the limbus. The anterior portion of the eye consists of the cornea iris pupil and crystalline lens. A black-looking aperture the pupilthat allows light to enter the eye it appears dark because of the absorbing pigments in the retina.
Anatomy of the Eye Major Landmarks and Features 3 of 3 Comeal limbus Posterior chamber with aqueous humor Tris Lens Anterior chamber with aqueous humor INFO Suspensory ligaments Pupil Cornea. The iris which is the colored part of the eye controls the amount of light that enters the eye. A glossary is included.
The neck area is called the cervix or cervical region. The cornea is located just in front of the iris which is the colored part of the eye. The shaft of the clavicle acts a point of origin and attachment for several muscles deltoid trapezius subclavius pectoralis major sternocleidomastoid and sternohyoid.
ANATOMY 3D ATLAS allows you to study human anatomy in an easy and interactive way. As part of the bony thorax the thoracic vertebrae help protect the internal viscera such as the heart lungs and oesophagus.
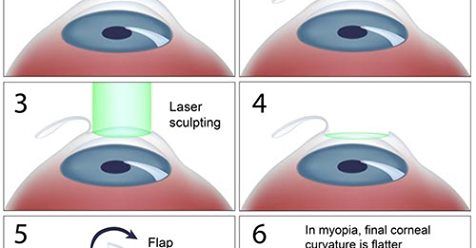 Lasik Eye Surgery Cost Benefits Risks How To Relief Lasik Eye Surgery Lasik Lasik Surgery
Lasik Eye Surgery Cost Benefits Risks How To Relief Lasik Eye Surgery Lasik Lasik Surgery
 Brain Major Landmarks Occipital Lobe Occipital Frontal Lobe
Brain Major Landmarks Occipital Lobe Occipital Frontal Lobe
 Human Body Printables For Kids Naturwissenschaften Fur Die Grundschule Korper Vorschule Wissenschaftsaktivitaten
Human Body Printables For Kids Naturwissenschaften Fur Die Grundschule Korper Vorschule Wissenschaftsaktivitaten
 Pin By Einar Yoris On Topology And Rigging Face Topology Character Modeling Cartoon Head
Pin By Einar Yoris On Topology And Rigging Face Topology Character Modeling Cartoon Head
 The Upper Extremity Laminated Anatomy Chart Shoulder Joint Anatomy Joints Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology
The Upper Extremity Laminated Anatomy Chart Shoulder Joint Anatomy Joints Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology
 Landmarks 1 Xiphoid Process 2 Costal Margin 3 Tip Of The Ninth Costal Cartilage 4 T Medicine Book Anatomy Medical Knowledge
Landmarks 1 Xiphoid Process 2 Costal Margin 3 Tip Of The Ninth Costal Cartilage 4 T Medicine Book Anatomy Medical Knowledge
 Occipital Bone Forensic Anthropology Occipital Developmental Psychology
Occipital Bone Forensic Anthropology Occipital Developmental Psychology
 Brodmann Area Function Atlas Updated Jan 2010 Functions Associated With Brodmann Areas And Links To Abstracts In 2020 Abstract Paper Reflexology Chart Function
Brodmann Area Function Atlas Updated Jan 2010 Functions Associated With Brodmann Areas And Links To Abstracts In 2020 Abstract Paper Reflexology Chart Function
 Pin By Ozari Williams On Knee Joint Anatomy Anatomy Of The Knee Gross Anatomy
Pin By Ozari Williams On Knee Joint Anatomy Anatomy Of The Knee Gross Anatomy
 Muscles Of The Thigh And Hip Anterior Coloring Anatomy Coloring Book Thigh Muscles Muscle
Muscles Of The Thigh And Hip Anterior Coloring Anatomy Coloring Book Thigh Muscles Muscle
 Amines By John18 Lecture Presentation Lecture Presentation Pearson Education
Amines By John18 Lecture Presentation Lecture Presentation Pearson Education
 The Lungs Quiz Or Worksheet Medical School Studying Biology Worksheet Art Books For Kids
The Lungs Quiz Or Worksheet Medical School Studying Biology Worksheet Art Books For Kids
 Pituitary Gland Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy Pituitary Gland Gland Internal Carotid Artery
Pituitary Gland Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy Pituitary Gland Gland Internal Carotid Artery
 Human Kidney Anatomy Medical Videos Anatomy Course Kidney Anatomy
Human Kidney Anatomy Medical Videos Anatomy Course Kidney Anatomy
 Pin By Carmen On Artvein Vascular Ultrasound Subclavian Artery Arteries
Pin By Carmen On Artvein Vascular Ultrasound Subclavian Artery Arteries
 4th Grade Social Studies Worksheets Free Printables Map Reading Geography Worksheets Topographic Map Activities
4th Grade Social Studies Worksheets Free Printables Map Reading Geography Worksheets Topographic Map Activities



Post a Comment for "Anatomy Of The Eye (major Landmarks And Features 1 Of 3)"