Describe The Structure Of Eye
Anatomically the eyeball can be divided into three parts the fibrous vascular and inner layersIn this article we shall consider the anatomy of the eyeball in detail and its clinical correlations. Anatomically the eye comprises two components fused into one.
 Cross Section Through The Human Eye Human Body Systems Human Anatomy And Physiology Body Systems
Cross Section Through The Human Eye Human Body Systems Human Anatomy And Physiology Body Systems
The sclera is the outermost layer of tissue also called the white of the eye.

Describe the structure of eye. The eye is a hollow spherical structure measuring about 25 cm in diameter. The Internal Structure of the Eye After the Iris and inside the Sclera is the Inner Structure of the eye. They include the eyebrows eyelids conjunctiva lacrimal apparatus and extrinsic eye muscles.
Structures auxiliary to the eye The orbit. The eye is enclosed by a tough white sac the sclera. The human eye is a roughly spherical organ responsible for perceiving visual stimuli.
The main parts of the human eye are the cornea iris pupil aqueous humor lens vitreous humor retina and optic nerve. Eyeball Bulbus oculi The eye is a highly specialized sensory organ located within the bony orbitThe main function of the eye is to detect the visual stimuli photoreception and to convey the gathered information to the brain via the optic nerve CN IIIn the brain the information from the eye is processed and ultimately translated into an image. Structure of the Eye.
The eye contains a transparent biconvex and elastic structure just behind the iris. The outer fibrous coat sclera cornea. A human eye is roughly 23 cm in diameter and is almost a spherical ball filled with some fluid.
The eye is made up of three coats or layers enclosing various anatomical structures. The eye consists of three layers of tissue which make up the wall of the eye. Hence it does not possess a perfect spherical shape.
The cornea is a. The eye is a hollow spherical organ about 25 cm 1 in in diameter. The eye is linked together with the nervous system which allows the brain to take in information from the eyes and make the appropriate decisions on how to act upon this information.
The front transparent part of the sclera is called cornea. The structures and functions of the eyes are complex. Each eye constantly adjusts the amount of light it lets in focuses on objects near and far and produces continuous images that are instantly transmitted to the brain.
They include the eyebrows eyelids conjunctiva lacrimal apparatus and extrinsic eye muscles figures 97 and 98. Light is focused by the lens and goes through. It lies in a bony cavity within the facial skeleton known as the bony orbit.
The surface of the cornea is where light begins its journey into the eye. It has a wall composed of three layers and internal spaces filled with fluids that support the walls and maintain the shape of the eye. The lens is held in position by suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary body.
The Cornea is the second structure that light strikes. Accessory Structures of the Eye Accessory structures protect lubricate and move the eye. The outermost layer known as the fibrous tunic is composed of the cornea and sclera which provide shape to the eye and support the deeper structuresThe middle layer known as the vascular tunic or uvea consists of the choroid ciliary body pigmented epithelium and iris.
Light enters the eye through the cornea. Its wall is composed of three coats. Parts of the Eye and Their Functions There are several physical and chemical elements that make up the eye.
The eyeball is a bilateral and spherical organ which houses the structures responsible for vision. It is known as a lens. It is enclosed within the eye sockets in the skull and is anchored down by muscles within the sockets.
It is the outer covering a protective tough white layer called the sclera white part of the eye. It consists of the following parts. The forebrain of the neural tube develops into primitive structures of the eyeball 1 Optic vesicles The forebrain is divided into two regions- but it is the DIENCEPHALON which forms evaginations creating optic vesicles 2 Lens Placode.
The eye is protected from mechanical injury by being enclosed in a socket or orbit which is made up of portions of several of the bones of the skull to form a four-sided pyramid the apex of which points back into the head. The iris controls the size of the pupil which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens. The middle vascular coat choroid ciliary body iris.
The lens divides the eye ball into two chambers an anterior aqueous and posterior vitreous chamber. Figure 227 Internal Anatomy of the Human eye The spherical eyeball is built of three layers 1 a tough outer white sclera or sclerotic for support and protection. The major parts of the eye are shown in figure 915.
If too steep myopianearsightedness. 2 middle choroid coat containing blood vessels for nourishment and 3 light-sensitive retina. The cornea is the transparent window in this white sac which allows the objects you are looking at to be carried in the form of light waves into the interior of the eye.
Structure of Human Eye. Light enters the eye by passing through the transparent cornea and aqueous humor. It is the clear transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris pupil and anterior chamber and provides most of an eyes optical power if too flat hyperopiafarsightedness.
This layer is a very stable fibrous membrane that continues to retain the shape of the eye and provides protection. Thus the floor of the orbit is made up of parts of the maxilla zygomatic and palatine bones while the roof is made up of the orbital plate of the frontal bone and behind this by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
 The Structure Of The Eye And The Functions Of These Accessory Structures Eye Structure Ciliary Muscle Eyes
The Structure Of The Eye And The Functions Of These Accessory Structures Eye Structure Ciliary Muscle Eyes
 Biomedical Devices For The Eyes Lesson Eye Exercises Human Eye Optic Neuritis
Biomedical Devices For The Eyes Lesson Eye Exercises Human Eye Optic Neuritis
 C 2 3 Structure And Function Of The Eye Hsc Biology Eye Function Structure And Function Biology Syllabus
C 2 3 Structure And Function Of The Eye Hsc Biology Eye Function Structure And Function Biology Syllabus
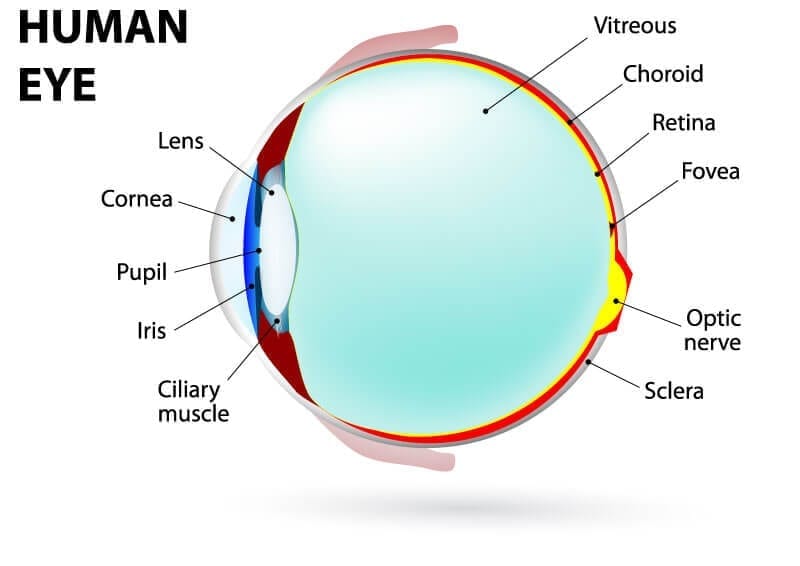 Understanding The Different Parts Of Your Eye All About Eyes
Understanding The Different Parts Of Your Eye All About Eyes
 Anatomy Eye Diagram To Label Eye Anatomy Diagram Eye Anatomy Anatomy
Anatomy Eye Diagram To Label Eye Anatomy Diagram Eye Anatomy Anatomy
 Trendy Eye Anatomy Diagram Illustrations Ideas Eye Anatomy Diagram Human Eye Diagram Diagram Of The Eye
Trendy Eye Anatomy Diagram Illustrations Ideas Eye Anatomy Diagram Human Eye Diagram Diagram Of The Eye
 Module 1 Labeled Diagram Of The Eye Diagram Of The Eye Dot Worksheets Eye Anatomy
Module 1 Labeled Diagram Of The Eye Diagram Of The Eye Dot Worksheets Eye Anatomy
 Label The Parts Of The Eye Parts Of The Eye Eyes Labels
Label The Parts Of The Eye Parts Of The Eye Eyes Labels
 Label The Parts Of The Eye And Describe How The Eye Works On This Free Printable Workshee Free Homeschool Printables Parts Of The Eye Free Homeschool Resources
Label The Parts Of The Eye And Describe How The Eye Works On This Free Printable Workshee Free Homeschool Printables Parts Of The Eye Free Homeschool Resources
 Sclera White Of The Eye Medical Anatomy Eye Structure Human Eye Diagram
Sclera White Of The Eye Medical Anatomy Eye Structure Human Eye Diagram
 Anatomy Of The Eye Eye Anatomy Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
Anatomy Of The Eye Eye Anatomy Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
 The Eye Diagram And Functions Functions Of The Human Eye Anatomy Body System Human Eye Diagram Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
The Eye Diagram And Functions Functions Of The Human Eye Anatomy Body System Human Eye Diagram Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
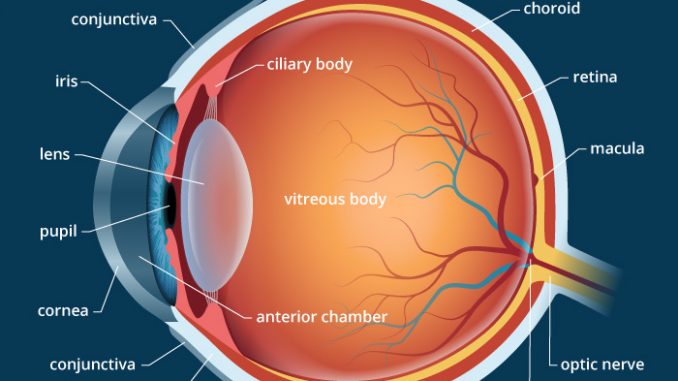 Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
 2010 In Review Eye Anatomy Anatomy Human Eye
2010 In Review Eye Anatomy Anatomy Human Eye
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Functions Of The Parts Of The Eye Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Parts Of The Eye
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Functions Of The Parts Of The Eye Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Parts Of The Eye
 Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram
Human Eye Ball Anatomy Physiology Diagram



Post a Comment for "Describe The Structure Of Eye"